AI Automation and the Future of Work: A Strategic Guide for 2025 and Beyond
AI Automation and the Future of Work: A Strategic Guide
Are You Prepared for the AI-Powered Workplace?
What if you could automate 30% of your team’s manual tasks within the next year, freeing them for high-impact strategic work? This isn’t a hypothetical scenario; it’s the emerging reality for businesses leveraging the current wave of artificial intelligence. The conversation has shifted from if AI will transform work to how and how quickly. A recent study by McKinsey suggests that generative AI alone could automate up to 29.5% of current work hours across the U.S. economy by 2030, accelerating a trend already in motion.
This data-driven evolution isn’t about replacing humans but augmenting our capabilities, creating a symbiotic relationship between human creativity and machine efficiency. This comprehensive guide will deconstruct the core frameworks of modern workplace AI, provide a actionable implementation timeline, and equip you with the strategies to not just adapt, but lead in the era of AI automation and the future of work.
Core Frameworks of Modern Workplace AI
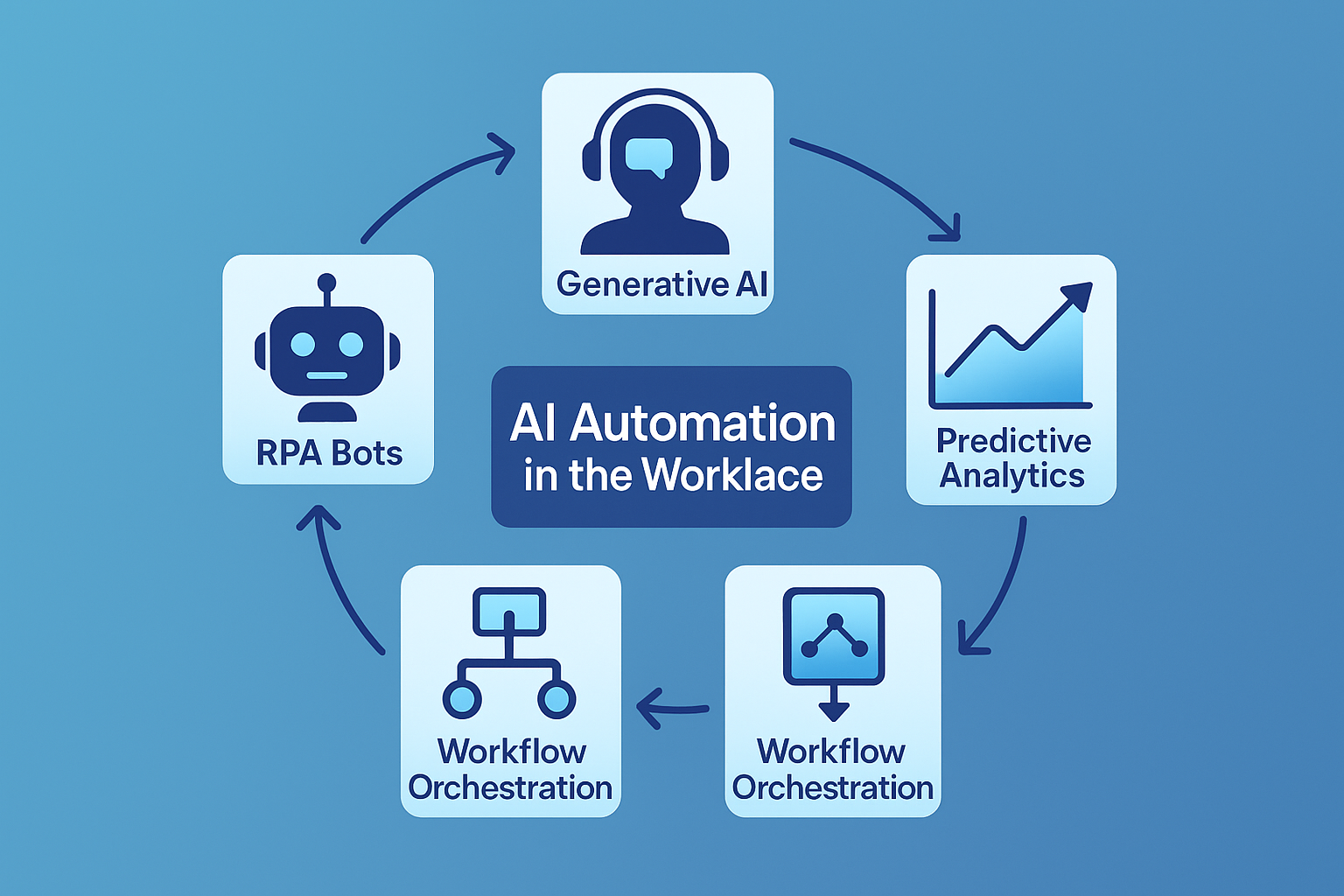
The term “AI” is a broad umbrella. To strategically adopt it, we must understand its core components. Modern business AI is not a single tool but an integrated stack of technologies.
- Generative AI & Large Language Models (LLMs): These are the engines behind tools like ChatGPT and Claude. They understand, generate, and translate human language, automating content creation, code generation, customer support, and data summarization.
- Robotic Process Automation (RPA): This is the “digital workforce” that automates repetitive, rule-based tasks across software applications. Think of it as teaching software to clicks buttons, copy-paste data, and fill forms without human intervention.
- Predictive Analytics & Machine Learning (ML): These systems learn from historical data to forecast future outcomes. They are crucial for demand forecasting, predictive maintenance, customer churn prediction, and dynamic pricing models.
- AI-Powered Workflow Orchestration: This is the “connective tissue” that integrates Generative AI, RPA, and analytics into a seamless, automated business process. Platforms like Zapier or Make now incorporate AI to intelligently route tasks and data.
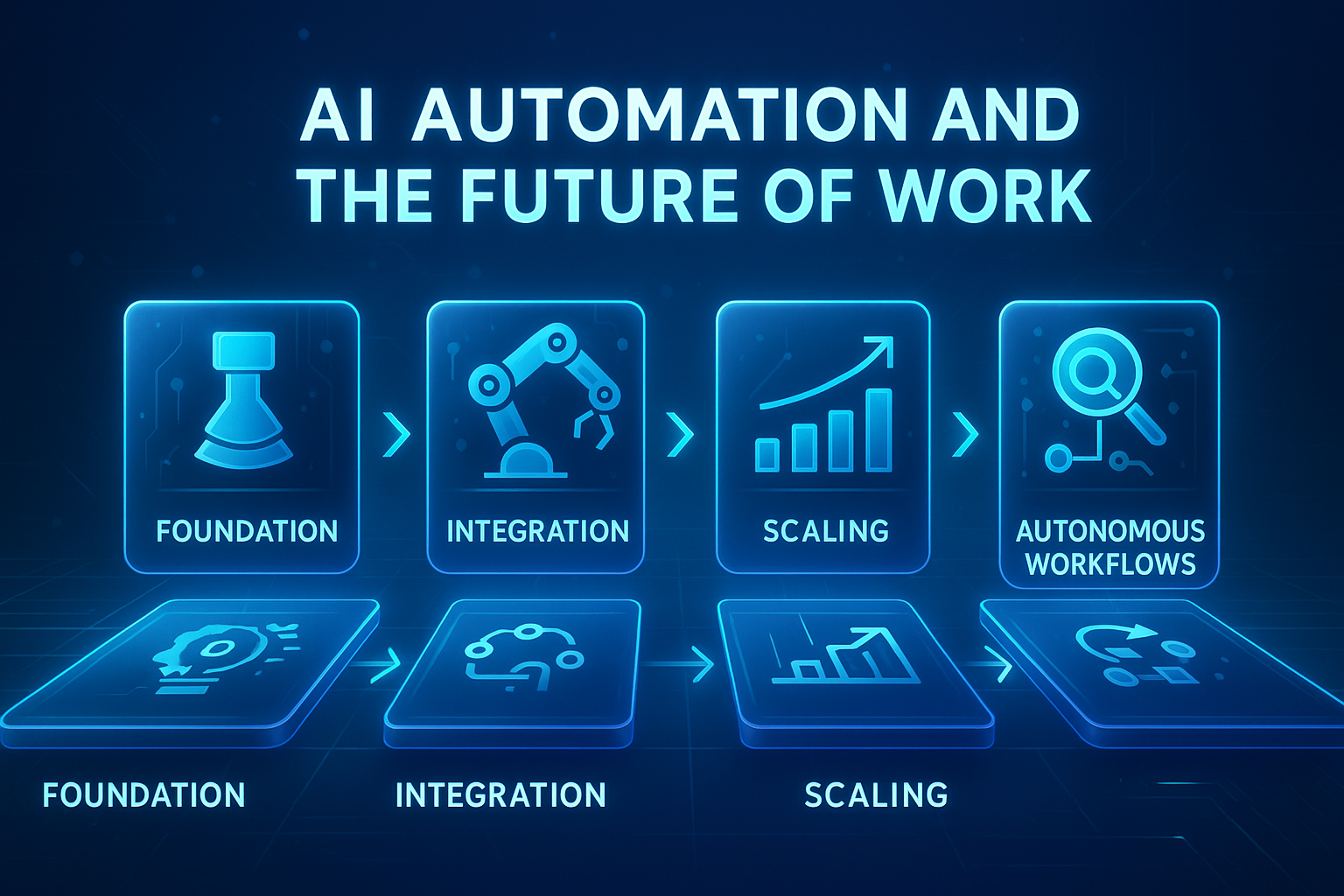
The AI Implementation Timeline: A Phased Approach (2024-2026+)
Adopting AI is a marathon, not a sprint. A phased approach mitigates risk and ensures sustainable growth.
- Phase 1: Foundation & Discovery (Now – Mid-2025)
- Focus: Identifying low-hanging fruit and building internal competency.
- Actions: Audit existing processes for automation potential. Pilot Generative AI tools for content and code. Train employees on AI fundamentals.
- Projection: Gartner predicts that by 2025, 50% of knowledge workers will use AI-powered virtual assistants daily, up from less than 5% in 2023.
- Phase 2: Strategic Integration & Scaling (Late 2025 – 2026)
- Focus: Integrating AI into core business functions and scaling successful pilots.
- Actions: Deploy department-specific AI solutions (e.g., AI for sales forecasting, marketing personalization). Develop a center of excellence for AI governance.
- Phase 3: Autonomous Transformation (2026+)
- Focus: Achieving enterprisewide AI maturity and competitive advantage.
- Actions: Implement AI for strategic decision-making. Develop fully autonomous workflows. Continuously innovate with emerging AI capabilities.
A Step-by-Step Guide to Adopting AI in Your Organization
Step 1: Assess Your Process Landscape
Begin by mapping your core business processes. Identify tasks that are highly repetitive, data-intensive, and rule-based. These are your prime candidates for RPA and basic automation.
Step 2: Identify Augmentation Opportunities
Next, look for areas where human judgment is bottlenecked by information overload. Could a Generative AI tool summarize lengthy reports for a manager? Could a predictive model help a financial analyst assess risk faster?
Step 3: Select and Pilot the Right Tools
Don’t boil the ocean. Choose one or two promising use cases and run a controlled pilot. For example, pilot an AI email drafting assistant for your sales team or an RPA bot for invoice processing.
Step 4: Foster a Culture of AI Fluency
Technology is only half the battle. Invest in training to upskill your workforce. Encourage experimentation and create safe channels for employees to suggest AI applications.
Step 5: Scale and Integrate
Based on pilot success, develop a rollout plan to scale the solution across relevant departments. Ensure it integrates smoothly with your existing tech stack (CRM, ERP, etc.).
Measuring the Impact: Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) for AI
To justify investment and guide strategy, you must measure impact. Focus on both efficiency and effectiveness metrics.
| Metric Category | Specific KPIs | Target Impact (Example) |
|---|---|---|
| Operational Efficiency | Process cycle time, Cost per task, Error rate | Reduce invoice processing time by 60%. |
| Employee Productivity | Tasks completed per hour, Time saved per employee | Free up 10 hours per week per knowledge worker. |
| Business Outcomes | Customer satisfaction (CSAT), Employee engagement, Revenue growth | Increase CSAT by 15 points through AI-powered 24/7 support. |
| Innovation Index | Number of new ideas generated, Speed of project completion | Accelerate product development cycles by 25%. |
Optimization Strategies for Peak AI Performance
Simply deploying AI is not enough. Continuous optimization is key.
- Implement a Feedback Loop: Use human feedback to continuously train and improve your AI models. This is crucial for maintaining accuracy and relevance.
- Integrate GPT-based APIs: Don’t just use off-the-shelf chatbots. Integrate GPT-based APIs into your custom applications to build tailored solutions for your unique workflows.
- Prioritize Data Quality: Garbage in, garbage out. An AI model is only as good as the data it’s trained on. Establish robust data governance practices.
- Embrace a Hybrid Intelligence Model: Design workflows where AI handles the initial heavy lifting (data analysis, draft creation) and humans provide the final review, creative input, and strategic oversight.
Real-World Use Cases and Industry Applications
AI’s tentacles reach every sector. Here’s how it’s being applied today:
- Marketing & Sales: AI-powered CRMs like Salesforce Einstein personalize customer outreach, predict lead scores, and automate follow-up emails.
- Healthcare: Algorithms analyze medical images (X-rays, MRIs) with radiology-level accuracy, aiding in faster diagnosis.
- Finance: JPMorgan Chase’s COIN program uses AI to interpret commercial loan agreements, a task that once consumed 360,000 hours of lawyer time annually.
- Manufacturing: Companies like Siemens use AI for predictive maintenance, analyzing sensor data to anticipate equipment failures before they cause downtime.
Common Pitfalls and How to Avoid Them
Many organizations stumble on their AI journey. Here’s how to sidestep common errors.
- Pitfall 1: Solving for Technology, Not a Problem.
- Solution: Always start with a clear business problem. Ask “What pain point are we solving?” not “Where can we use AI?”
- Pitfall 2: Neglecting Change Management.
- Solution: Communicate transparently from the start. Frame AI as a tool for empowerment, not replacement.
- Pitfall 3: Underestimating Data Security and Ethics.
- Solution: Develop a robust AI ethics framework and involve your security team early in the procurement and implementation process. For a deeper dive, consider our internal piece on Building a Responsible AI Strategy.
Maintenance and Scalability: Future-Proofing Your AI Investments
AI models can degrade over time as data patterns change—a phenomenon known as “model drift.”
- Schedule Regular Audits: Periodically retest your AI systems against key performance benchmarks.
- Design for Modularity: Build your AI architecture with interchangeable parts so you can easily upgrade components as new, better models emerge.
- Stay Agile: The AI landscape evolves monthly. Foster a culture of continuous learning and be prepared to pivot your strategies as new opportunities arise.
Seizing the AI Advantage
The future of work is not a distant horizon; it is unfolding now, shaped by the deliberate adoption of AI, automation, and the future of work strategies. The organizations that will thrive are those that view AI not as a cost-saving utility, but as a core strategic partner for innovation and growth. By understanding the core frameworks, following a structured implementation timeline, and vigilantly measuring impact, you can transform potential disruption into unparalleled opportunity. The time to act is today.
Ready to operationalize your AI strategy? [Download our free AI Readiness Assessment Worksheet] to identify your top automation opportunities and build a business case for leadership.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. Will AI completely replace human jobs?
While AI will automate certain tasks, it is more accurate to say it will transform jobs. The World Economic Forum’s “Future of Jobs Report 2023” anticipates a net decrease of only 2% in current roles by 2027, but a significant shift in the skills required. Roles focusing on creativity, emotional intelligence, and complex problem-solving will become more prominent.
2. What is the typical ROI for an AI implementation?
ROI varies widely but can be substantial. A well-executed RPA project can often see a 200-300% ROI in the first year. For generative AI, gains are often seen in productivity uplifts of 20-40% for specific tasks.
3. How can small businesses with limited budgets afford AI?
The rise of Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) AI tools has dramatically lowered the barrier to entry. Small businesses can start with affordable subscriptions for AI writing assistants, customer service chatbots, or basic analytics platforms.
4. What’s the biggest ethical concern with workplace AI?
Algorithmic bias is a primary concern. If an AI is trained on historical data that contains human biases, it will perpetuates and even amplify them. Mitigating this requires diverse data sets and ongoing human oversight.
5. Which department should lead AI adoption?
There is no single answer. A cross-functional team is ideal, often led by a combination of IT (for technical integration), Operations (for process knowledge), and a dedicated business leader (e.g., a Chief AI Officer) to drive strategy.
6. How long does it take to see results from an AI project?
Tactical pilots can show results in weeks (e.g., a chatbot reducing ticket volume). Strategic, enterprise-wide transformations can take 12-24 months to reach full maturity and ROI.
7. What is the difference between AI and Machine Learning?
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is the broad science of mimicking human abilities. Machine Learning (ML) is a specific subset of AI that trains a machine how to learn by using algorithms to parse data, learn from it, and make a determination or prediction.
Share this content:












Post Comment